Pharmacovigilance
Welcome to our online course on Pharmacovigilance for healthcare providers in Kenya, a comprehensive and free learning platform designed to enhance your professional skills and knowledge. Our Pharmacovigilance course is offered by CRK clinical research organization and independently sponsored by Pfizer.
As a healthcare provider in Kenya, it’s crucial to stay updated with the latest developments in pharmacovigilance. This free course offers you the opportunity to do just that, providing an in-depth exploration of drug safety principles, adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and risk management strategies.
The online course on Pharmacovigilance is tailored to the unique needs and challenges of the Kenyan healthcare system. It delves into the role of regulatory authorities in drug safety, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the local and global pharmacovigilance landscape.
Our course is not just about theory; it’s about practical application. You’ll learn how to identify, assess, understand, and prevent adverse drug reactions, enhancing patient safety and improving treatment outcomes. The knowledge and skills you gain will directly apply to your daily practice, making you a more effective and informed healthcare provider.
Enroll in our online course on Pharmacovigilance for healthcare providers in Kenya and take the next step in your professional journey.
What Will I Learn?
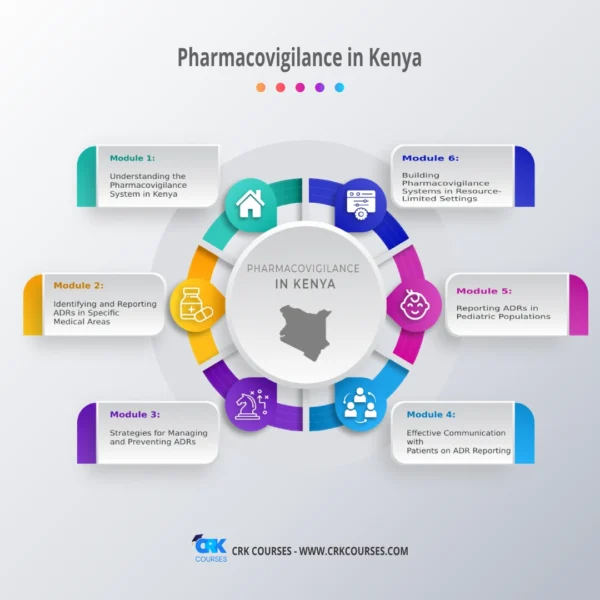
- Understanding the Pharmacovigilance System in Kenya
- Identifying and Reporting ADRs in Specific Medical Areas
- Strategies for Managing and Preventing ADRs
- Effective Communication with Patients on ADR Reporting
- Reporting ADRs in Pediatric Populations
- Building Pharmacovigilance Systems in Resource-Limited Settings
Course Content
Module 1: Understanding the Pharmacovigilance System in Kenya
Module 1 pre-test
Module 1 Overview
00:00Lesson 1: Introduction to Pharmacovigilance and Its Importance in Patient Safety
08:40Lesson 2: Pharmacovigilance Regulations and Reporting Requirements in Kenya
06:36Module 1 lesson 2 (Roleplay)
03:04Lesson 3: The process of reporting pharmacovigilance in Kenya
15:47Module 1 lesson 3 (Roleplay) Reporting Methods
03:28Module 1 Assessment Test
Module 2: Identifying and Reporting ADRs in Specific Medical Areas
Module 3: Strategies for Managing and Preventing ADRs
Module 4: Effective Communication with Patients on ADR Reporting
Module 5: Reporting ADRs in Pediatric Populations
Module 6: Building Pharmacovigilance Systems in Resource-Limited Settings
About the instructors
John Heshmat is a pharmacist and public health professional with over a decade of diverse experience in clinical research, health education, and humanitarian service across Africa. He holds a Master’s in International Public Health from Liverpool John Moores University and a Bachelor of Pharmacy from October 6 University.
As the Clinical Operations Manager at CRK Clinical Research Key (CRO), John leads high-impact clinical research and capacity-building programs targeting underserved populations in Kenya. He also serves as the Country Coordinator for Mécénat Chirurgie Cardiaque, a global organization that sponsors life-saving heart surgeries for children with congenital heart defects.
At CRKCourses.com, John combines scientific rigor with practical field insight to deliver CME/CPD-accredited e-learning programs for healthcare professionals. His teaching emphasizes evidence-based practice, health equity, and the real-world application of research in resource-limited settings.
With a passion for public service and training the next generation of African health leaders, John is committed to improving patient outcomes through education, innovation, and collaborative learning.
4 Courses
8867 students
CRK is Kenyan’s largest and most comprehensive provider of post-graduate training courses in clinical research, public health, pharmaceutical sciences, and various other domains. At CRK-CRO, we believe a properly trained and competent health workforce is essential to any successful healthcare system.
10 Courses
2360 students
GREAT OUTLINE, I HAVE LEARNT A LOT.
This course is a great milestone in my career as a Pharmaceutical Technologist and a champion in Pharmacovigilance .
Very insightful
Good
skillful appreciate
Good presentation but could add more details.
Educative
Informative.
The course was very informative. I enjoyed the sessions. Instructor: John Dawod
The course is very educative and relevant to all



